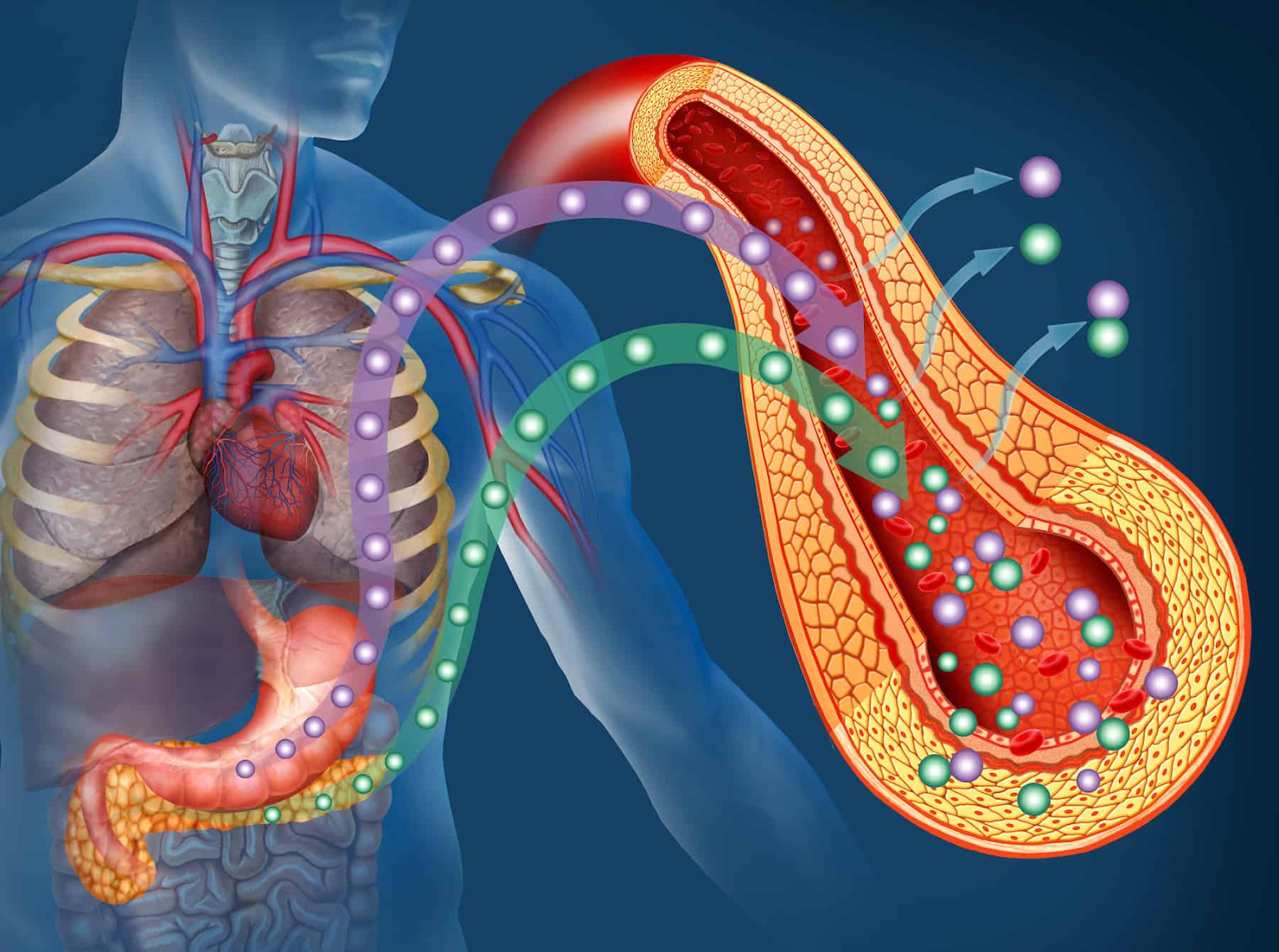
Insulin resistance is a common but often misunderstood condition. Many people live with it for years without realizing it. But recognizing the symptoms early can make a big difference in preventing more serious health problems like type 2 diabetes or heart disease.
Let’s explore what insulin resistance means, how it affects your body, and most importantly, how to spot its signs before it becomes something more dangerous.
What Exactly Is Insulin Resistance, and Why Should You Care?
Insulin resistance happens when your body’s cells stop responding properly to insulin, a hormone that helps regulate blood sugar levels. Normally, insulin acts like a key that unlocks your cells so they can absorb glucose (sugar) from your bloodstream and use it for energy.
When you’re insulin resistant, your cells don’t respond well to insulin. As a result, your body has to produce more insulin to manage the same amount of blood glucose. Over time, this can lead to high blood sugar levels and other health complications.
Here’s why it matters:
- It increases your risk of developing type 2 diabetes.
- It raises your chances of heart disease and stroke.
- It can be linked to other conditions like polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS) and nonalcoholic fatty liver disease.
In short, insulin resistance isn’t just about blood sugar—it’s a red flag for many potential health issues.
How Does Insulin Resistance Develop?
Understanding how insulin resistance starts can help you recognize your own risk factors.
Some common causes include:
- Excess body weight, especially around the waist
- Sedentary lifestyle
- An unhealthy diet high in refined carbohydrates and highly processed foods
- Family history of diabetes or metabolic syndrome
Your body mass index (BMI) also plays a role. Being overweight or obese puts extra stress on your insulin receptors, making them less effective.
As insulin resistance progresses, your body struggles to keep up with the demand for insulin production. Eventually, your pancreas may not be able to release enough insulin to maintain normal blood glucose levels.
This is when impaired glucose tolerance begins, and if left untreated, it can lead to full-blown diabetes mellitus.
What Are the Common Symptoms of Insulin Resistance?
Many people with insulin resistance don’t experience obvious symptoms at first. However, there are several subtle signs that could indicate a problem:
- Fatigue, especially after meals
- Feeling hungrier than usual
- Trouble concentrating or brain fog
- Weight gain, especially around the belly
- High blood pressure
- Skin tags or patches of darkened skin (acanthosis nigricans)
Because these signs can be mistaken for other issues, it’s important to understand how insulin resistance affects your body over time.
People with insulin resistance may notice they’re gaining weight even without eating more, or they feel sluggish despite getting enough sleep. These are clues that their body is struggling to manage blood sugar effectively.
Are There Blood Tests That Can Diagnose Insulin Resistance?
Since symptoms can be vague, doctors often rely on blood tests to detect insulin resistance. Here are some of the most common ones:
- Fasting glucose test: Measures your blood sugar after an overnight fast.
- Oral glucose tolerance test: Checks how well your body handles sugar after drinking a sugary solution.
- Hemoglobin A1c test: Shows your average blood sugar levels over the past few months.
- Blood test measures insulin levels directly, though this is less commonly used.
If any of these tests show abnormal results, it might mean you have impaired insulin sensitivity or insulin resistance syndrome.
Early detection through regular screening is key, especially if you have other risk factors like a family history of diabetes or high blood pressure.
How Is Insulin Resistance Related to Other Health Conditions?
Insulin resistance doesn’t happen in isolation. In fact, it’s often part of a group of conditions known as metabolic syndrome, which includes:
- High blood pressure
- Low HDL cholesterol level
- High triglycerides
- Excess abdominal fat
Having metabolic syndrome significantly increases your risk for cardiovascular disease and type 2 diabetes.
Additionally, insulin resistance is closely linked to:
- Polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS) in women
- Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease
- Gestational diabetes during pregnancy
These connections highlight why managing insulin resistance is crucial, not just for diabetes management but for overall health.
Who Is Most Likely to Develop Insulin Resistance?
While anyone can develop insulin resistance, certain groups are at higher risk:
- People who are overweight or obese
- Those with a family history of type 2 diabetes
- Individuals with hormonal disorders like PCOS
- People who lead sedentary lifestyles
- Those who eat a highly processed diet
Age also plays a role. As we get older, our bodies naturally become less sensitive to insulin. That’s why older adults should be especially mindful of changes in energy levels, weight, and blood pressure.
Even if you don’t fall into one of these categories, it’s still smart to pay attention to your body and get regular checkups.
Can You Reverse Insulin Resistance Naturally?
The good news is that insulin resistance is not permanent. With the right lifestyle changes, you can improve insulin sensitivity and even reverse insulin resistance.
Here are some effective strategies:
- Losing weight, especially around the waist
- Eating a healthy diet rich in whole grains, vegetables, and lean proteins
- Reducing intake of refined carbohydrates and highly processed foods
- Getting regular physical activity
- Managing stress and improving sleep quality
Clinical research shows that even a modest weight loss of 5–10% can significantly reduce insulin resistance and lower blood glucose levels.
Also, eating foods with a low glycemic index helps stabilize blood sugar and prevents spikes that strain your insulin system.
What Medical Treatments Are Available for Insulin Resistance?
While lifestyle changes are the foundation of treatment, some people may need medical help to treat insulin resistance effectively.
Common treatments include:
- Metformin, a medication often prescribed for type 2 diabetes
- GLP-1 receptor agonists, which help control blood sugar and aid weight loss
- Insulin therapy in advanced cases where the body can no longer produce enough insulin
It’s important to work with a healthcare provider to create a personalized plan. The American Diabetes Association recommends a combination of diet, exercise, and medication when necessary for diabetes care and disease control.
Your doctor may also suggest regular blood tests to monitor your progress and adjust your treatment plan accordingly.
How Can You Prevent Insulin Resistance From Worsening?
Prevention is always better than a cure. If you already have mild insulin resistance, here are steps you can take to prevent it from getting worse:
- Maintain a healthy weight through balanced nutrition and regular movement
- Avoid excess sugar and unhealthy fats
- Stay hydrated and limit alcohol consumption
- Get enough sleep each night
- Visit your doctor regularly for checkups
Remember, small changes add up. Even walking 30 minutes a day or swapping out sugary snacks for healthy foods can make a difference.
What Role Does Diet Play in Improving Insulin Sensitivity?
Diet plays a central role in managing insulin resistance. The types of food you eat can either help your body regulate blood sugar or make it harder.
Foods that support insulin sensitivity include:
- Whole grains like oats and brown rice
- Vegetables and leafy greens
- Healthy fats from nuts, seeds, and fish
- Lean proteins such as chicken, turkey, and legumes
On the flip side, eating foods high in added sugars, refined carbs, and trans fats can worsen insulin resistance and raise blood sugar levels.
Choosing meals with a low glycemic index helps your body absorb blood glucose more steadily, reducing the burden on your insulin system.
Why Is Physical Activity So Important for People with Insulin Resistance?
Exercise is one of the most powerful tools for improving insulin sensitivity. When you move your body, your muscles use glucose for energy, which lowers blood sugar levels naturally.
Benefits of physical activity include:
- Helps your body use insulin more efficiently
- Promotes weight loss and muscle building
- Reduces risk of heart disease and stroke
- Boosts mood and energy levels
You don’t need to run a marathon—just 30 minutes of moderate activity five days a week can make a real impact.
Activities like brisk walking, swimming, cycling, or strength training all count. The key is consistency.
How Can You Support Your Body’s Natural Ability to Manage Blood Sugar?
Supporting your body’s natural processes is essential for long-term health. Here are a few ways to do that:
- Stay hydrated – Water helps your kidneys flush out excess glucose.
- Get enough fiber – Fiber-rich foods slow down sugar absorption.
- Manage stress – Chronic stress increases cortisol, which can raise blood sugar.
- Take supplements wisely – Some, like magnesium and chromium, may support insulin function, but always talk to your doctor first.
By taking a holistic approach, you give your body the best chance to maintain healthy blood glucose levels and avoid complications.
What Should You Do If You Think You Have Insulin Resistance?
If you’re experiencing signs of insulin resistance or have risk factors like excess weight or a family history of diabetes, it’s time to take action.
Here’s what to do:
- Talk to your doctor about getting a blood glucose test
- Ask about an oral glucose tolerance test if needed
- Request a review of your blood pressure, cholesterol, and insulin levels
- Consider working with a registered dietitian or diabetes educator
Early intervention can prevent insulin resistance from turning into type 2 diabetes or other serious conditions.
Final Thoughts: Take Control of Your Health Before It’s Too Late
Insulin resistance is a silent but powerful condition that affects millions of people worldwide. Left unchecked, it can lead to high blood sugar levels, heart disease, and even diabetes mellitus.
But the good news is that you have the power to change your health trajectory. Whether through losing weight, eating healthier foods, or increasing physical activity, you can improve your insulin sensitivity and reduce your risk of complications.
Don’t wait until symptoms become severe. Start making small, sustainable changes today. Your future self will thank you.
Works Cited
American Diabetes Association. “Standards of Medical Care in Diabetes—2023.” Diabetes Care, vol. 46, no. 1, Jan. 2023, pp. S1–S154.
Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. “About Insulin Resistance.” CDC.gov, 2023, www.cdc.gov/diabetes/basics/insulin-resistance.html.
National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases. “Insulin Resistance & Prediabetes.” NIDDK.nih.gov, U.S. Department of Health and Human Services, Apr. 2021, www.niddk.nih.gov/health-information/diabetes/overview/what-is-diabetes/prediabetes-insulin-resistance.
Mayo Clinic. “Insulin Resistance: What You Need to Know.” Mayoclinic.org, 2022, www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/insulin-resistance/symptoms-causes/syc-20354983.
Harvard T.H. Chan School of Public Health. “The Nutrition Source: Carbohydrates.” hsph.harvard.edu/nutritionsource/carbohydrates/, 2023.
Cleveland Clinic. “Insulin Resistance Syndrome.” ClevelandClinic.org, 2023, my.clevelandclinic.org/health/diseases/23355-insulin-resistance-syndrome.
If you’re looking for personalized, prevention-focused healthcare that puts your needs first, NY Choice Medical is here to help. From advanced cardiac care to comprehensive treatment plans tailored to your unique health goals, NY Choice Medical is committed to supporting your well-being.
Take control of your health today—visit NY Choice Medical to learn more about their services and schedule your consultation. Early detection and customized care can make all the difference in preventing serious conditions like heart disease and insulin resistance. Your journey to better health starts now.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
2. What are the common symptoms of insulin resistance?
Many people with insulin resistance don’t notice symptoms at first. However, common signs include:
- Feeling tired or sluggish, especially after meals
- Increased hunger
- Weight gain, particularly around the belly
- High blood pressure
- Dark patches on the skin (acanthosis nigricans)
- Difficulty concentrating
If you’re experiencing these, it may be time to talk to a healthcare provider.
3. How is insulin resistance diagnosed?
There’s no single test for insulin resistance, but doctors often use blood tests to check related markers. These include:
- Fasting glucose test
- Oral glucose tolerance test
- Hemoglobin A1c test (measures average blood sugar over time)
- Insulin level testing
These tests help determine if your blood sugar levels are in a healthy range or if you have impaired glucose tolerance.
4. Can insulin resistance be reversed?
Yes, insulin resistance can improve with lifestyle changes. Losing weight, eating a healthy diet rich in whole grains and vegetables, reducing refined carbs and sugary foods, and increasing physical activity can all help boost insulin sensitivity. Even a small amount of weight loss—like 5–10% of your body weight, can make a big difference.
5. What are the risks if insulin resistance is left untreated?
If not managed, insulin resistance can lead to serious health problems such as:
- Type 2 diabetes
- Heart disease
- Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease
- Polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS)
- Metabolic syndrome
Early detection and treatment are key to preventing long-term complications and maintaining good health.